Joystick with Arduino
Joysticks can be very handy for many applications like retro gaming, robot or robot-arm control,
remote controlling cars or drones.
The Analog Joystick is similar to two potentiometers connected together, one for the vertical
movement (y-axis) and other for the horizontal movement (x-axis).
The joystick also comes with a switch to trigger some event like to switch on / off a device.
But the best thing is: using a joystick with the Arduino is extremely easy!
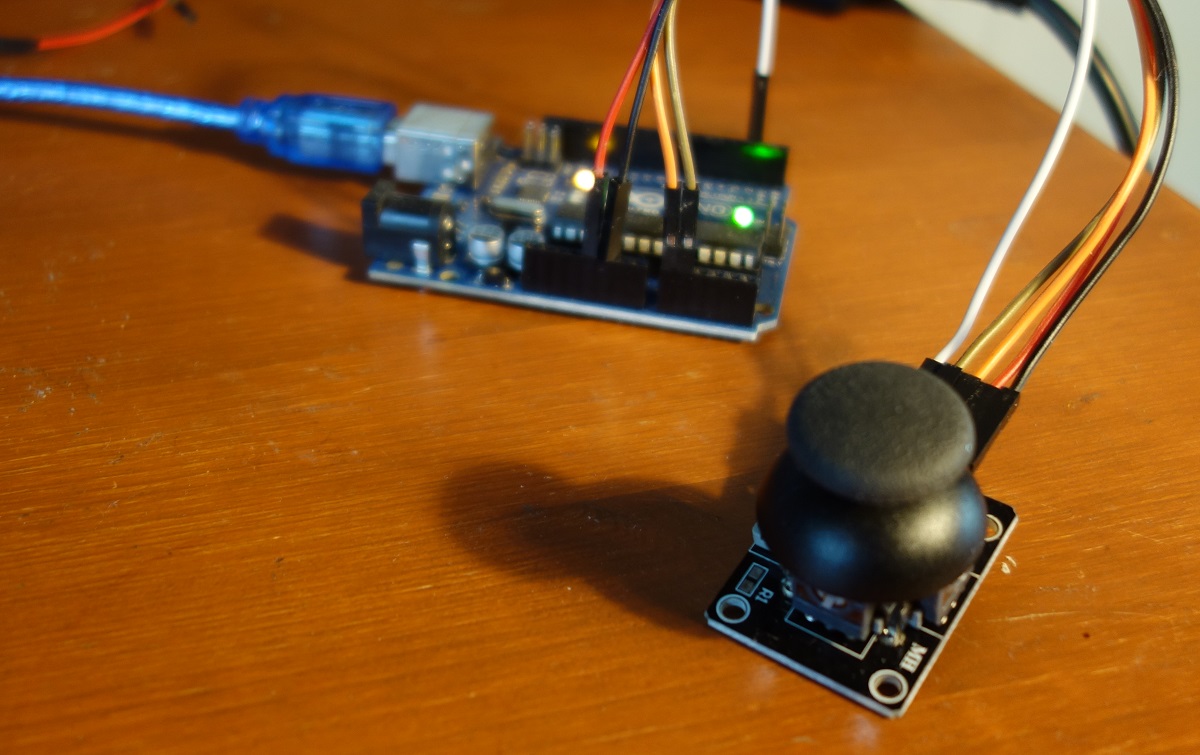
Required parts: 1 x Arduino Uno (or compatible) 1 x analog joystick like KY-023 5 x jumper cable male - female

How it works
First of all, you have to understand that a joystick gives analog values in the form of a voltage as input to the Arduino. The Arduino uses an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to generate a digital value from the analog voltage signal. Since the Arduino Uno has an ADC resolution of 10 bits, the values on each analog channel can vary from 0 to 1023.
As long as the joystick is in a neutral position, the values for the x and y axis should be around 500. If the stick is moved on x axis from one end to the other, the x values will change from 0 to 1023 and the same happens when moved along the y axis.
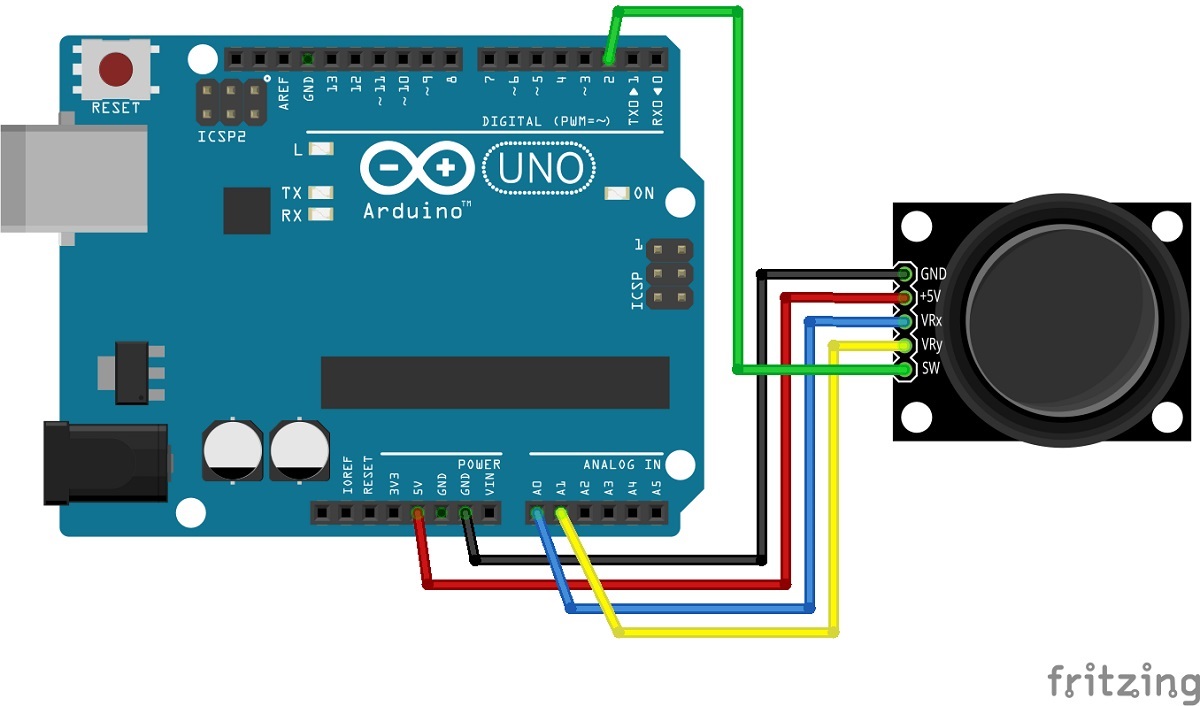
Wiring Diagram for Joystick
Arduino KY-023 ----------------------- A0 VRX A1 VRY Pin 2 SW 5V +5V GND GND
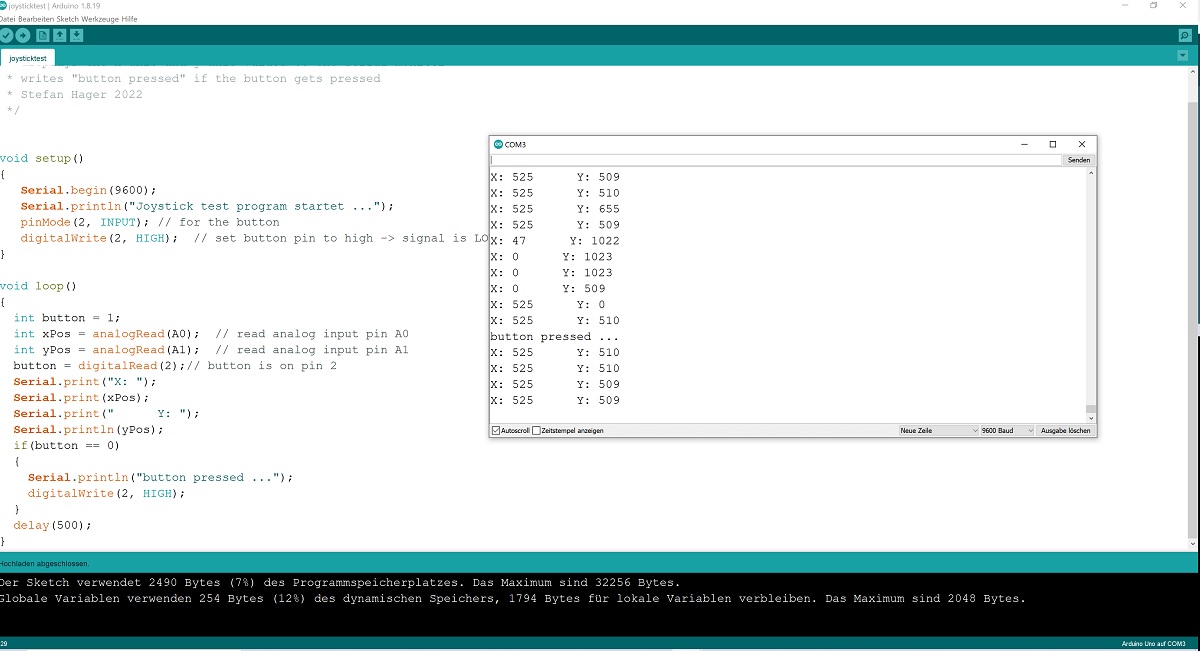
Software for Joystick - Control
/* Arduino Joystick Tutorial
* displays the x-axis and y-axis values to the serial monitor
* writes "button pressed" if the button gets pressed
* Stefan Hager 2022
*/
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Joystick test program startet ...");
pinMode(2, INPUT); // for the button
digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // set button pin to high -> signal is LOW when pressed
}
void loop()
{
int button = 1;
int xPos = analogRead(A0); // read analog input pin A0
int yPos = analogRead(A1); // read analog input pin A1
button = digitalRead(2);// button is on pin 2
Serial.print("X: ");
Serial.print(xPos);
Serial.print(" Y: ");
Serial.println(yPos);
// button pressed -> signal low
if(button == 0)
{
Serial.println("button pressed ...");
digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // reset pin 2 to HIGH
}
delay(500);
}
Running the Program
Start the program, move the joystcik and press the button. Look into the serial monitor of the Arduino IDE to see the resulting values.