Operating the LIDAR
The Lidar Class
The lidar class should encapsulate all the essential operations required for lidar operation. In particular, the class should provide a method that provides a point representation that accurately depicts the environment.
import serial
import time
class Lidar:
def __init__(self):
#self.PORT = "/dev/ttyUSB0"
self.PORT = "COM13"
self.BAUDRATE = 460800
self.serial = serial.Serial(self.PORT, self.BAUDRATE, timeout=1)
def send_cmd(self, cmd):
self.serial.write(cmd)
time.sleep(0.05)
def start_scan(self):
self.send_cmd(b'\xA5\x20')
def stop_scan(self):
self.send_cmd(b'\xA5\x25')
def reset(self):
self.send_cmd(b'\xA5\x40')
def close(self):
self.serial.close()
# get_scan_packet ---
# get one tupel for : angle , distance, quality
def get_scan_packet(self):
while True:
b0 = self.serial.read(1)
if not b0:
return None
b0 = b0[0]
# echtes RPLIDAR Sync-Kriterium
if ((b0 & 0x01) ^ ((b0 >> 1) & 0x01)) == 1:
rest = self.serial.read(4)
if len(rest) != 4:
return None
b1, b2, b3, b4 = rest
quality = b0 >> 2
angle_raw = ((b1 >> 1) | (b2 << 7))
angle = angle_raw / 64.0
dist_raw = b3 | (b4 << 8)
distance = dist_raw / 4.0
if 0 <= angle <= 360 and 10 <= distance <= 8000:
return angle, distance, quality
# get_full_scan ------
# scan until you have num_points; num_points should not be too small
# to get a good scan
def get_full_scan(self, num_points):
frame = []
while len(frame) < num_points:
pkt = self.get_scan_packet()
if not pkt:
continue
angle, distance, quality = pkt
frame.append((angle, distance, quality))
return frame
Visualization
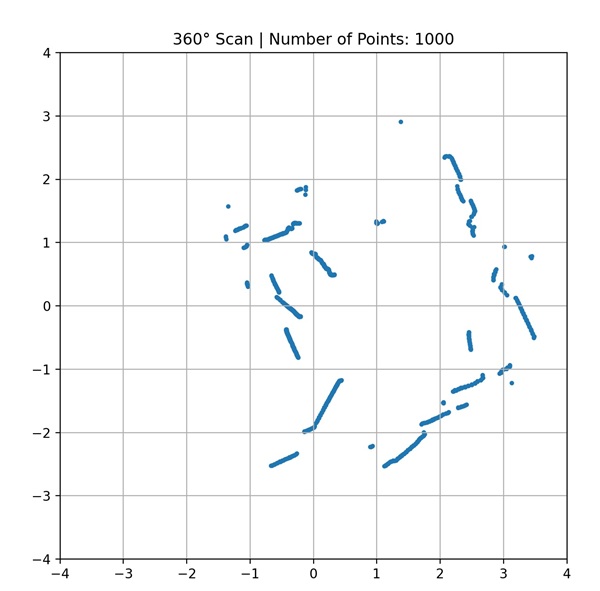
This program serves as a test for the lidar class by displaying the collected data in a coordinate system.
import time
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from Lidar import Lidar
# --- Plot one Frame (angle and distance) ---
def plot_frame(frame, sc, ax):
xs = []
ys = []
for angle, distance, _ in frame: # quality will not be displayed
r = distance / 1000.0 # convert from mm to m
rad = math.radians(angle)
x = r * math.cos(rad)
y = r * math.sin(rad)
xs.append(x)
ys.append(y)
sc.set_offsets(list(zip(xs, ys)))
ax.set_title(f"360° Scan | Number of Points: {len(frame)}")
# --- Main ---
def main():
ldr = Lidar()
ldr.reset()
time.sleep(2)
ldr.start_scan()
plt.ion()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7,7))
sc = ax.scatter([], [], s=6)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xlim(-4, 4)
ax.set_ylim(-4, 4)
ax.set_title("LiDAR 360° Scan")
ax.grid(True)
try:
while True:
# make a scan with 1000 points
frame = ldr.get_full_scan(1000)
plot_frame(frame, sc, ax)
plt.pause(0.001)
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\nStop Scan...")
finally:
ldr.stop_scan()
ldr.close()
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
The result of acan should look like this example: